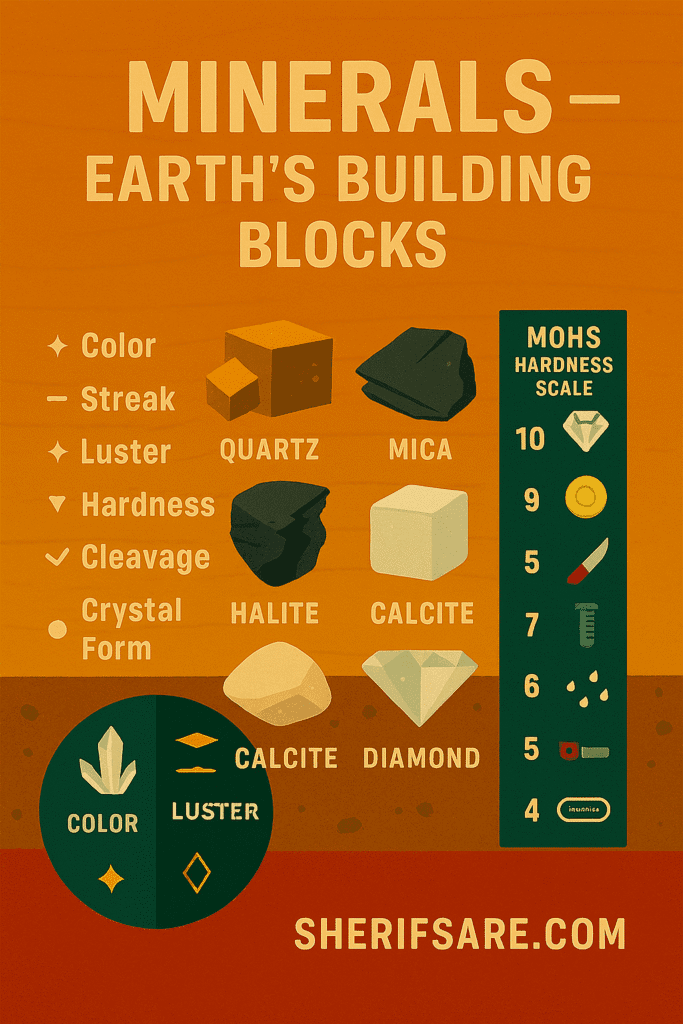
Minerals are naturally occurring, inorganic solids with a definite chemical composition and crystal structure. They’re the ingredients that make up rocks and the key to understanding Earth’s composition.
How to Identify Minerals
| Property | What to Look For | Example Minerals |
|---|---|---|
| Color | Surface appearance | Quartz (clear), Pyrite (gold) |
| Streak | Color of powdered form | Hematite (red streak) |
| Luster | How it reflects light | Metallic (Galena), Glassy (Quartz) |
| Hardness | Resistance to scratching (Mohs scale) | Talc (1), Diamond (10) |
| Cleavage | How it breaks along planes | Mica (perfect cleavage) |
| Crystal Form | Shape of crystal faces | Halite (cubic), Quartz (hexagonal) |
Mohs Hardness Scale (1–10)
| Hardness | Mineral | Can Be Scratched By… |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Talc | Fingernail |
| 3 | Calcite | Copper coin |
| 5 | Apatite | Knife blade |
| 7 | Quartz | Steel file |
| 10 | Diamond | Nothing (hardest known) |
Why Minerals Matter
- Mining: Minerals like gold, bauxite, and quartz are economically vital
- Construction: Minerals form cement, tiles, and glass
- Technology: Rare earth minerals power electronics
- Geology: Mineral composition helps classify rocks and interpret Earth’s history
What’s Next
In the next post, we’ll explore Geologic Time and Earth’s History; how rocks and fossils reveal the story of our planet.