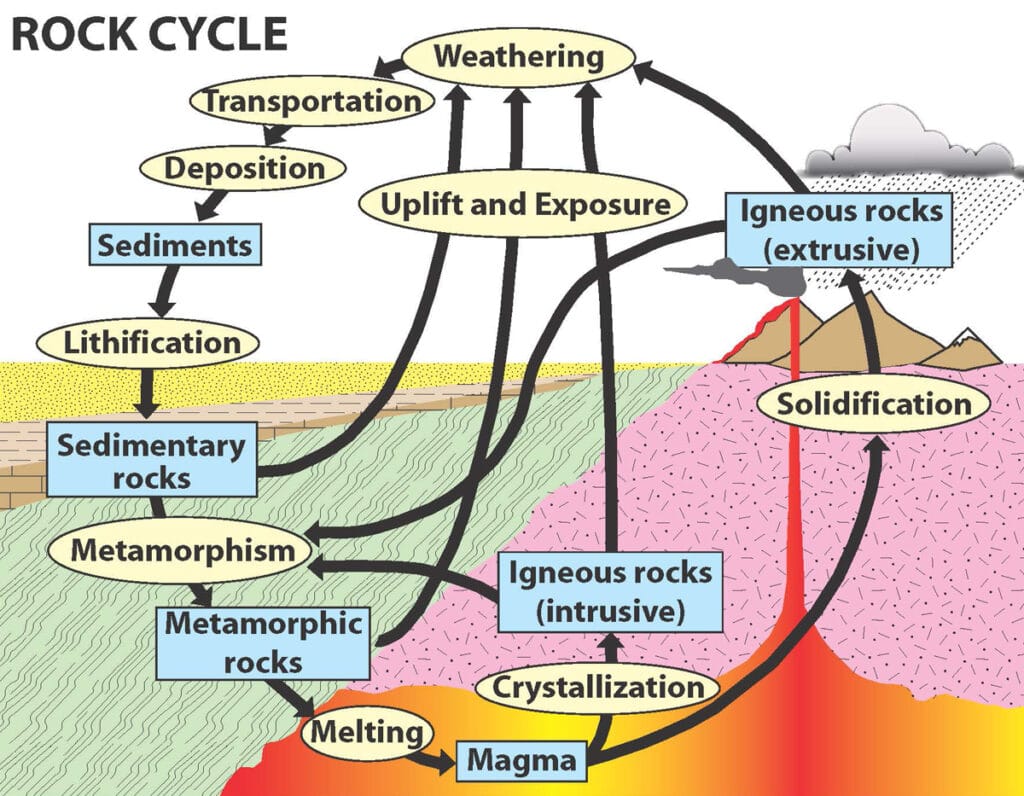
Why Geophysical Surveys Matter
Geophysics lets us explore what lies beneath Earth’s surface without digging. Whether you’re hunting for gold, mapping groundwater, or planning a city, geophysical methods reveal hidden layers, faults, and resources.
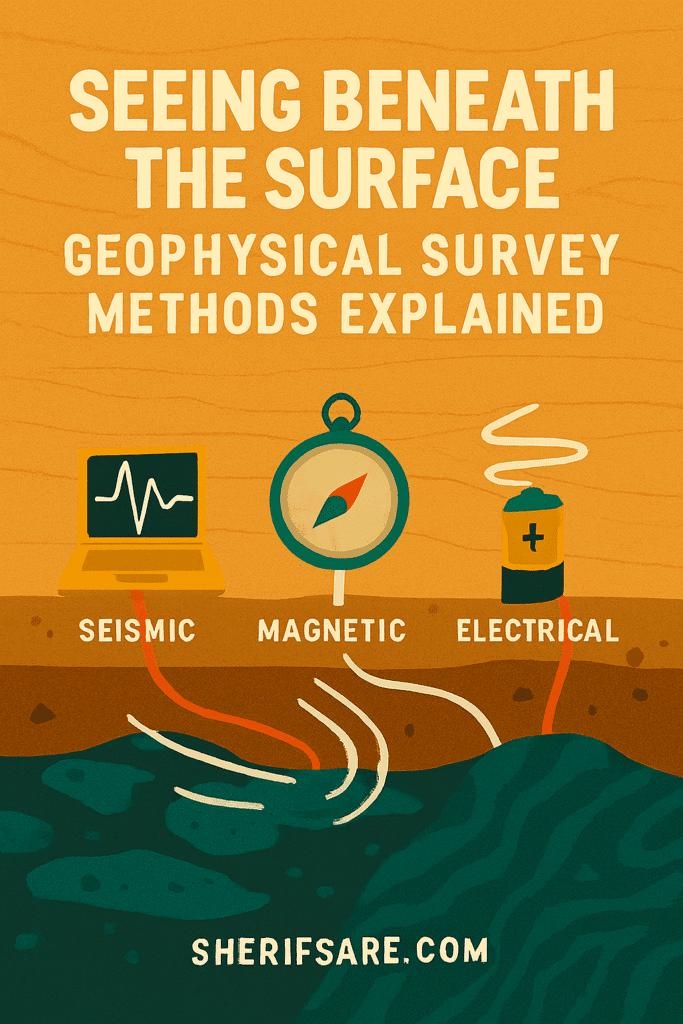
Core Geophysical Methods
| Method | What It Detects | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Seismic | Wave velocity through rock layers | Oil & gas, fault zones, site stability |
| Magnetic | Magnetic anomalies in subsurface rocks | Mineral exploration, structural mapping |
| Electrical | Resistivity of underground materials | Groundwater, pollution, archaeology |
| Gravity | Density variations in Earth’s crust | Basin modeling, tectonic studies |
| GPR | Radar reflections from shallow features | Utilities, archaeology, shallow mapping |
How Each Method Works
- Seismic: Sends shock waves into the ground; measures how fast they bounce back.
- Magnetic: Detects iron-rich or magnetized zones using field sensors.
- Electrical: Injects current into the ground; measures resistance to flow.
- Gravity: Measures tiny changes in gravitational pull caused by rock density.
- GPR: Emits radar pulses; records reflections from buried objects or layers.
Real-World Applications
- Mining: Locate ore bodies, faults, and safe drilling zones.
- Urban Planning: Assess subsurface stability before construction.
- Environmental Studies: Detect buried waste, groundwater flow, or contamination.
- Archaeology: Reveal buried structures without excavation.
What’s Next
In the next post, we’ll explore the importance of geology.