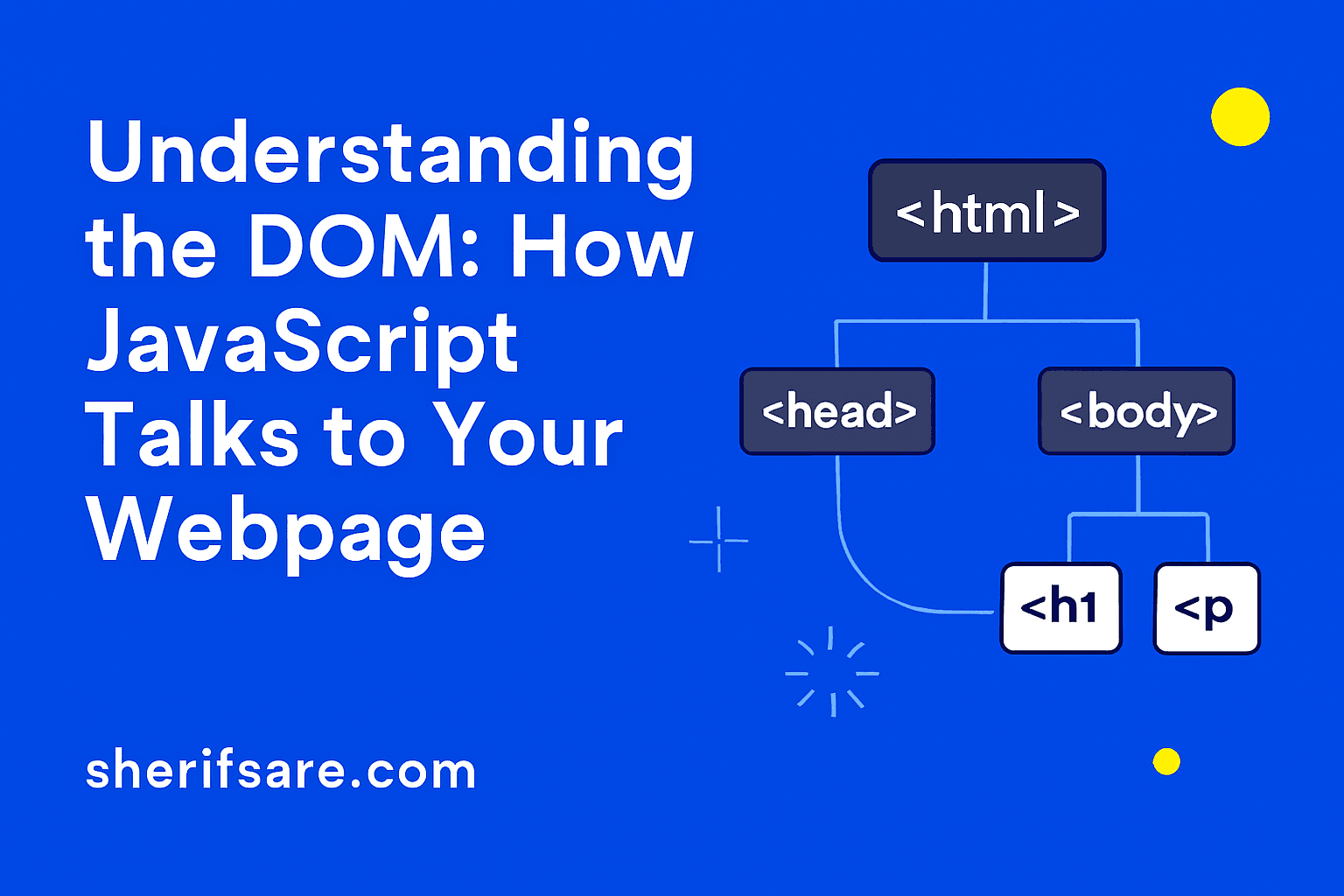
JavaScript becomes truly powerful when it interacts with your webpage’s structure. This is done through the DOM — the Document Object Model. It’s how JavaScript “sees” and “talks to” your HTML.
In this post, we’ll explore:
- What the DOM is
- How to select and modify elements
- How to respond to user actions with events
What Is the DOM?
The DOM is a tree-like structure that represents your HTML document. Every tag becomes a node that JavaScript can access and manipulate.
Selecting Elements
JavaScript can select elements using methods like:
document.getElementById("title");
document.querySelector("p");
document.querySelectorAll("button");Once selected, you can change their content, style, or behavior.
Modifying Elements
Example:
document.getElementById("title").innerText = "Welcome to My Site!";
document.querySelector("p").style.color = "yellow";Handling Events
JavaScript listens for user actions like clicks, typing, or scrolling:
document.querySelector("button").addEventListener("click", function() {
alert("Button clicked!");
});This is how you make your site interactive — responding to users in real time.
Try It Yourself
Create a simple HTML page with:
- A heading
- A paragraph
- A button
Use JavaScript to:
- Change the heading text
- Change the paragraph color
- Show an alert when the button is clicked
Final Thoughts
Mastering the DOM and events unlocks the full potential of JavaScript. You’ll be able to build responsive, dynamic, and user-friendly websites.
In the next post, we’ll explore Forms and Validation — how to collect and verify user input.