Programming isn’t just about storing data; it’s about acting on it.
With if statements, your code can make decisions based on conditions. It’s how you build logic into your programs.
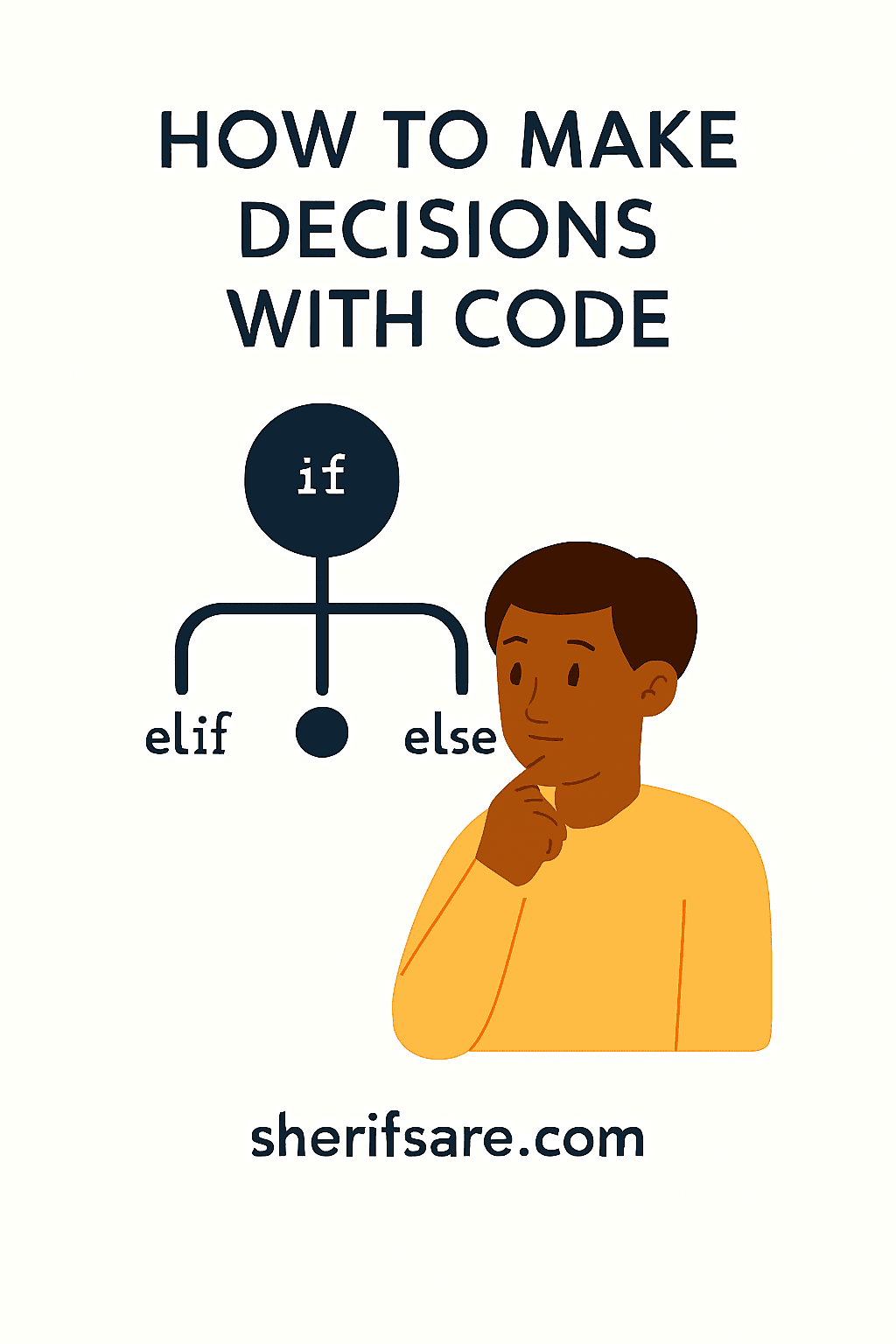
What Is an If Statement?
An if statement checks whether something is true. If it is, the code inside runs.
Here’s a simple example:
age = 18
if age >= 18:
print("You’re an adult.")
If the condition age >= 18 is true, the message is printed.
Add More Logic
You can add else and elif (else if) to handle other cases:
age = 16
if age >= 18:
print("You’re an adult.")
elif age >= 13:
print("You’re a teenager.")
else:
print("You’re a child.")
Now your code responds differently depending on the value of age.
Real-Life Analogy
Think of a traffic light:
- If it’s green → go
- If it’s yellow → slow down
- If it’s red → stop
Your code works the same way. It checks conditions and acts accordingly.
What’s Next?
In the next post, we’ll explore loops; how to repeat actions automatically and efficiently.